Here are our answers to the most common questions asked by APA members about tires.
How long do tires last?
If their wear does not require them to be changed before this, tires are designed to last about six years. Beyond that, the rubber compound offers diminished adhesion and it may start to crack; the casing may also weaken.
To know the age of your tires, you can look at the date code on their sidewall. The date code is found in a marking that follows one of the following formats:
- DOT XXXX XXX XXXX
first two characters: manufacturing plant identification mark
last four digits: date code (week / year)
The other characters are left at the manufacturer’s discretion.
Example: DOT U2VK 3ML 2602: In this case, the tire has been manufactured on the 26th week of 2002 — in other words, in June 2002.
- DOT XXXX XXXX XXX (older three-digit date code format)
first two characters: manufacturing plant identification mark
last three digits: date code (two for the week / one for the year)
The other characters are left at the manufacturer’s discretion.
Example: DOT P1RW B4LR 109: This particular tire was made on the 10th week of 1999.
How can I know if my tires are worn out?
All tires have tread wear indicators, which are small bars of rubber found between the tread blocks of a tire. When the tread is worn flush with the tread wear indicators, the tire has reached its wear limit and must be replaced; failing to do so may result in the near total loss of wet weather traction and may eventually lead to a blowout.

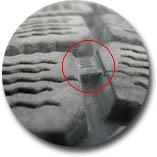
It is important to note that at its wear limit, a tire already no longer offers sufficient traction in the rain or in the snow. For safety reasons, it is therefore recommended that a tire be changed when its tread reaches a depth of 3 mm (a bit less that 4/32″).
For the same reasons, a winter tire should have a tread depth of at least 5 mm (6/32″) at the beginning of winter to ensure good performance until the end of the season.
What is best: studded tires or other winter tires?
Studded tires are otherwise regular winter tires fitted with a high number of sharp metallic or ceramic claws meant to enhance traction on icy roads. Not all winter tires can be fitted with studs; only those which are rated “studdable” (an inscription found on their sidewall) by their manufacturer are designed with the possible fitment of studs in mind.
For the vast majority of motorists, modern, non-studded winter tires are the preferred choice. In addition to offering plenty of grip on both snow and ice, they perform much better on asphalt and are significantly quieter. They are also not subjected to the restrictions affecting studded tires.
For a few motorists who frequently drive under very difficult conditions, studded tires can offer an added margin of safety on ice. Consult a specialist to know if you are among those who need studded tires. Regulations aimed at these tires vary from one province to another; here is a summary.
| Province / Territory | Restrictions | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Alberta | no restriction | |
| British Columbia | from Oct. 1 to April 30 only | |
| Manitoba | from Oct. 1 to April 30 only | Ceramic core studs or ceramic studs only |
| Ontario | restriction | https://www.ontario.ca/laws/regulation/r19004 |
| Quebec | from Oct. 15 to May 1 | Only Commercial vehicles: less than 3000 kg only Passenger vehicles: on both axles only |
| Saskatchewan | no restriction | |
| Newfoundland | from Nov. 1 to April 31 only | |
| Yukon | no restriction |
The pressure you will find written on the sidewalls of your tires is not the recommended pressure; it is the maximum pressure allowable for the tire, not the vehicle. The recommended pressure can be found in the owner’s manual and on a sticker affixed on a door jamb (most often the driver’s door), on the inside of the fuel filler door or, sometimes, on the inside of the glove compartment door. On a few sports cars, this sticker can be found under the trunk lid or underneath the engine hood.
Inflate your tires to the standard recommended pressure unless you are carrying a heavy load; in this case, follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for a loaded vehicle if there are such recommendations. For sustained highway driving, drivers who want to improve fuel economy and reduce tire wear may choose to raise the tire pressure to the value(s) recommended for a loaded vehicle or highway driving.
You should check tire pressure only when the tires are cold. Immediately after having used your car, the air pressure rises as the air is heated up; the manufacturer’s recommendations regarding tire pressure are meant for a cold tire. For the same reason, in winter, the tire pressure inside a heated garage will be superior to what it would be outside (where it counts).
Verify tire pressure using a dedicated tire pressure gauge like those that can be purchased at auto parts stores and at tire retailers. Some service station air pumps have integrated pressure gauges, but these are generally inaccurate.
If the overall diameter of the wheel and tire combination differs, the odometer and speedometer readings will be inaccurate. In extreme cases, a tire of different width or height could contact suspension parts or the wheel well. Also, the new tire must have a width that is compatible with that of the wheel rim. When in doubt, consult a specialist or your dealership. The APA’s recommended tire retailer, Talon Tire, can help you with conversion information.
Rotating the tires on your car should be done at regular intervals to ensure that the four tires are evenly worn. This prolongs tire life and evens out treadwear on individual tires. On all-wheel drive cars, rotation is essential to make the all-wheel drive system work properly.
On front-wheel drive vehicles, tire rotation should be done every 12 000 km.
On rear-wheel drive, all-wheel drive cars and sports cars in general, tire rotation should be done every 10 000 km.
Should you find it difficult to free yourself to have this important maintenance operation performed, schedule it with a routine maintenance operation like an oil change. Tire rotation should be included in at least each second routine servicing of the car; otherwise, expect to pay for about half an hour of work in labour costs.
Pour un véhicule à traction arrière, à traction intégrale et toutes les voitures sport, la permutation doit généralement être faite aux 10 000 km.
S’il vous est difficile de vous libérer pour faire effectuer cette opération d’entretien essentielle, songez à la synchroniser avec une opération d’entretien routinier, comme un changement d’huile. D’ailleurs, la permutation des pneus doit normalement être inclue dans au moins un entretien routinier sur deux. Sinon, vous devez vous attendre à la facturation d’environ une demi-heure de travail par l’atelier.
Generally, this is not a recommended practice. The small difference in rolling diameter between the worn and the new tires can be enough to damage the center differential of such a vehicle or to adversely affect the intended bias between front and rear torque distribution.
The four tires on an all-wheel drive vehicle should be of the original size; they should all be of the same brand and model and they must have even wear. Replace them in sets of four to avoid expensive damage.
Since it is vital for an all-wheel drive car to have four tires with roughly even wear, you should replace it with a used tire in a state of wear that corresponds to that of the three remaining tires.
In a perfect world, the wheels should be removed from the car and stored (see the next article). If possible, the suspension of the car should remain compressed to avoid the onset of rust on the shock absorber piston rods.
Should it be impossible for you to store the car without its tires, inflate them to 35 PSI (2.4 bar) or 40 PSI (2.75 bar), depending on the maximum pressure on the sidewall. Ideally, during the storage period, move the car for a few centimeters once a month or, if the tires are high performance tires, every two weeks to avoid the formation of flat spots.
Follow these few rules and your tires will remain in perfect condition throughout their service life.
a) If your tires are stored mounted on wheels, keep them inflated to a pressure of 15 PSI (1 bar).
b) Ideally, do not store them in an upright position, but stack them laying flat on their side. If this is impossible, leave them upright and rotate them about once a month to prevent the formation of a flat spot.
c) Protect them with plastic bags thick or dark enough to protect the tires from ambient light.
d) Avoid extreme temperatures and humidity. Above all, refrain from storing them outside, where they will likely be subjected to temperature swings and high humidity.
e) Do not leave them on a moist or greasy floor; isolate them with a wooden plank.
f) Keep them at least two meters away from electric motors and radiators. These devices generate ozone which oxidizes tire rubber and deteriorates the tires.
The offset of a wheel is the distance between the centerline of the rim and the wheel hub, or how far the edge of the wheel sticks out from the center. When the wheels of a given vehicle are replaced, they must be replaced with wheels of similar offset; if not, the tire could well come in contact with suspension parts or with the inside of the wheel well itself. Suspension geometry can also be affected by offset changes.
Under many leasing contracts, the tires are required to have at least 4/32″ of tread remaining at the end of the lease. In Québec, any requirement beyond normal wear is void under the Consumer Protection Act. Here are some things to keep mind:
3 years / 60 000 km lease: You may make it all the way through with the original tires.
3 years / 72 000 km, 4 years / 80 000km, 4 years / 96 000km: You most likely will not make it on the original tires. We suggest you buy winter tires right away and benefit from the added safety they provide in winter. When you turn in the vehicle, the original all season tires should have some life left in them.
If you need tires at the end of your lease, do what used car dealers do: buy a set of good used tires.
Location de 3 ans / 72 000 km, 4 ans / 80 000 km, 4 ans / 96 000 km: les pneus d’origine dureront moins longtemps que la location. Nous vous suggérons d’acheter des pneus d’hiver dès maintenant et de profiter des bénéfices qu’ils offrent en matière de sécurité hivernale. Lors de la remise du véhicule, les pneus quatre saisons d’origine devraient encore être conformes aux exigences du contrat.
S’il est nécessaire de remplacer les pneus à la fin de la location, la solution est de faire ce que font les concessionaires de voitures usagées: acheter quatre pneus usagés en bon état.
Some automakers will allow it, but only if the tires correspond to the season when the lease terminates. Most will not accept winter tires on a summer return.
Les roues de ce type sont des roues avec lesquelles une voiture semblable à la vôtre a été livrée et qui ont été données au marchand en échange de roues d’un autre fournisseur. Les roues “take-off” n’ont généralement tout au plus que quelques semaines d’utilisation et, si elles conviennent réellement à votre voiture, peuvent constituer un bon achat.
This will only be possible if those tires have the same dimensions as the tires of the new car or, at the very least, if their size is compatible with the wheels of the new car and with the car itself. Consult the owner’s manual or ask your dealership if the tires are not exactly the same size.
If you are changing from a vehicle more than five years old to a new vehicle, chances are the new tires and the wheels will be larger.
